There’s a lot of information online on different gut health websites about which SIBO diet works the best & how to do one.
Most of this information is put together by people who’ve never seen a sibo patient (unlike our team who actually have).
A lot of these websites say things like “you cannot eat any fruit, bread, beans, pasta or potatoes – period!” during a SIBO diet.
Or “you have to eliminate all dairy except kefir, drink lots of apple cider vinegar, & only eat alkaline foods.”And this just isn’t true.
Remember, a lot of the information out there is written by people who’ve never treated a single sibo case in their whole life. Yet they’re telling you what foods will or won’t work for you.
The truth is, you can eat fruit. You can eat bread. You can eat beans. You can eat pasta if it’s made of certain grains. You can eat potatoes if you cook them a certain way.
Keep reading and we’ll dispel every myth other there concerning what works & doesn’t work against SIBO.
We’ll also explain our 3-phase SIBO diet we developed based on over 20 years of research & thousands of before & after stool tests.
Topics covered on this page
- What Is SIBO & How Does It Feel To Have It?
- What REALLY Causes SIBO & Why Is It So Difficult To Get Rid Of?
- How to Test For SIBO: Stool Tests vs the Breath Test
- Our 3-Phase SIBO Diet
- Should You Follow the FODMAP Diet For SIBO? Pros & Cons
- The 14 Day Big Clean-Up
- Step 1: The MEVY Diet (Meat, Eggs, Vegetables & Yogurt)
- Step 2: The Low Allergy Diet (Restores Your Gut’s Immune System)
- Step 3: The Food Reintroduction Phase
- Grab CanXida’s 3 Phase SIBO Diet & Food List
What Is SIBO & How Does It Feel To Have It?
As you’ve likely heard, SIBO stands for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth.
Many people think SIBO has something to do with bad or pathogenic bacteria overgrowing in the small intestine.
But this usually not the case. Many patients with SIBO do have an overgrowth of bad bacteria or yeast in their GI tract in addition to SIBO, as having SIBO predisposes you to additional gut issues.
But we’ll get to that later.
The small intestine has about 2000 to 3000 bacteria cells per milliliter of fluid (at least in healthy people). While the colon (large intestine) has about 1 billion bacteria per milliliter.
Both the large & small intestine are supposed to have bacteria in them. Bacteria is necessary for you to digest food. You can’t really break down food without them.
SIBO basically means that bacteria that shouldn’t be there have somehow found their way into your small intestine.
And they’re having a full on house party.
SIBO isn’t about necessarily about bad bacteria or good bacteria, it’s about the number of bacteria. It means you’ve got HIGH levels of bacteria in the small intestine when the number should be low.
Symptoms of SIBO often include:
- Severe digestion issues (constipation, diarrhea, IBS like symptoms)
- Food allergies
- Gas & bloating.
- Nausea
- Malnutrition
- Brain fog & difficulty concentrating
- Anxiety & irritability
- Skin issues such as rashes or eczema
- Severe abdominal pain and cramps
- Chronic fatigue
Patients with SIBO usually report more diarrhea than constipation.
Bloating is a major symptom. Patients report that when the bloating is bad, it’s “ALL CONSUMING.” As in it takes control of your life.
One women with severe SIBO for example had pants ranging from size 8 to 16 in her wardrobe. Because some days she literally couldn’t pull up her jeans. And when she ate certain foods, her stomach would swell up & she’d look like she was 4 months pregnant.
SIBO, gas and bloating go hand in hand.
This is because of how much space there is in the small intestine. The small intestine is 20 feet long on average. It’s where fresh, new, easy to digest food passes through & gets broken down.
Where as the colon (large intestine) is where the leftover stuff that we couldn’t break down ends up. That’s why we have high levels of bacteria in the colon. The bacteria break down the leftover food & then it passes through us.
These bacteria in the colon are what produce gas. But they can’t produce a whole lot of it because the colon is only 3 ft long. There’s just not that much space for the gas to accumulate and cause bloating.
Now imagine 15 ft instead of 3 ft of high levels of bacteria. Plus fresh, easy to digest food instead of leftovers.
The bacteria is going to have a feeding frenzy and produce a an extreme amount of gas and bloating.
And this is the problem.
What REALLY Causes SIBO & Why Is It So Difficult To Manage?
SIBO rarely has a single cause.
In most cases there are several factors that when combined, will trigger a patient to develop SIBO.
Our team has worked with THOUSANDS of SIBO cases & the big patterns we see are:
- poor diet (too much processed food, take out, sugar, etc).
- alcohol
- exposure to chemicals or toxins
- high stress
- gut infections such as an overgrowth of yeast (like candida), bad bacteria & parasites
- antibiotics
- oral contraceptive pill
- acid blocking drugs
Anything that reduced the speed at which food moves through the gut will cause SIBO over time. This is why patients with slow gut motility will develop SIBO over time.
Recently several studies have come out linking Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) to SIBO.
Another theory that has been circulating around is that SIBO is caused by food poisoning and toxins. And these have apparently caused nerve damage to the small intestine which has resulted in the small intestine cleansing itself less often. And this leads to bacterial overgrowth.
One of the major causes of SIBO (in our experience) is antibiotic use.
This is where we differ a lot with other experts. Many SIBO experts are OK using antibiotics with their patients. But antibiotics in fact are either ineffective or only provide temporary relief in at least half the cases.
We’re generally not fans of using conventional medicine for SIBO. Our experience has shown that natural treatment methods often lead to more effective and lasting results.
We’ve seen too many cases where a SIBO patient took antibiotics, felt better for a few days or a few weeks, and then the SIBO came back.
And often with stronger symptoms than before.
The problem with antibiotics (as you’ve probably read elsewhere) is they indiscriminately wipe out ALL the bacteria in your gut, including the beneficial ones.
But what most people don’t understand is these beneficial bacteria are what PREVENT SIBO (as well as most other gut disorders) in the first place.
Nearly every patient with SIBO has had a history of antibiotic use BEFORE they got sick. And the higher the antibiotic use was prior, the more severe the SIBO symptoms were.
So don’t think for a minute that you have to go for conventional medications. You really don’t.
How to Test For SIBO: Stool Tests vs the Breath Test
If you’ve been diagnosed with SIBO or did some research into it, you likely heard about the breath test.
This is a test where you exhale into a machine that analyses your breath and tells you if you’ve got one of the 3 types of SIBO.
The 3 types of SIBO are:
- Methane Dominant SIBO
- Hydrogen Dominant SIBO
- Hydrogen Sulfide Dominant SIBO
The type of SIBO you have depends on which bacteria have overgrown in the small intestine, as different species of bacteria produce different gases when they break down food.
People get really hung up and obsessed with these 3 types.
They focus too much on which type they have.
Breath tests are ok, but the problem with a breath test is it doesn’t tell the quantity or species of bacteria that are causing the gases.
It just shows if you have bacteria that create gases like methane or hydrogen. You don’t know the names of these bacteria or how many of them you got. Those gases can be produced in abundance by many different bacteria strains, all of which can respond to different forms of treatment.
This is why we recommend what’s called a Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis or CDSA test instead of the breath test.
Particularly for patients with severe symptoms & those who’ve been struggling with SIBO for a long period of time (such as 6 months or longer).
This is a very advanced test most GI docs don’t have much experience with. It’s an expensive test (usually between $600 and $800) & most insurance companies don’t cover it.
What’s special about a Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis is it checks what’s going on in your gut at the MICROSCOPIC level.
It’s going to tell you the levels of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus & Bifida you have, the levels of bad bacteria, their species, if you’ve got an overgrowth of yeast (like Candida Albicans), microscopic parasites (like Blastocystis), inflammation, leaky gut & a WHOLE LOT more.
Including exactly which bacteria species have overgrown and are causing problems in your small intestine & their numbers.
This is the most advanced, least invasive test you can do on the gut.
It’s basically a full spectrum analysis of your microbiome.
Want to know what you’re most likely to find if you get one of these tests performed?
Imbalances ACROSS THE BOARD.
You’re going to see a lack of beneficial bacteria. Over 60% of CDSA tests from SIBO patients these days come back with no beneficial bacteria at all. The lab couldn’t culture them & they couldn’t find them. This is especially true in gut disorder patients who suffer from fatigue.
You’re also likely to see an overgrowth of some sort. You may have multiple issues. Often times we see some kind of yeast has overgrown in addition to the bacteria.
We’ve seen many SIBO patients with very high levels of streptococci bacteria.
For example alpha homiletic strep & gamma homiletic strep.
And these bacteria have sat in the body for multiple years & become resistant to many different medications.
Unfortunately many of these patients end up going to see a functional doctor thinking it’s the right thing to do. And they get put on an antibiotic.
But little do they know that these antibiotics only provide short term relief and actually make the bugs stronger and resistant over time.
How We Know Our 3-Phase SIBO Diet Works
The 3-phase diet we’re about to share with you is based on over 30 years and thousands of hours spent in the clinic working solely with SIBO & chronic gut disorder patients. As well as researching countless books, speaking with experts, & old fashioned trial & error.
It wasn’t made up out of thin air by some blogger like other SIBO diets you’ll find online. It was created by naturopaths (such as the one you’ll be seeing in the videos on this page.
That’s why we feel confident saying that this diet can be effective. It’s designed to support people with SIBO, regardless of how long you’ve had symptoms, previous treatments you’ve tried, or the specialists you’ve seen.
This is not an exaggeration. We know this because of the feedback we’ve received from patients. As well as lab tests performed before, during & after patients began the diet & treatment method we outline on this page. Our staff had whole cabinets at one point full of stool test lab results from hundreds of SIBO patients before, during & after we put them on our diet & treatment plan. It’s how we developed this diet in the first place.
It’s straightforward, easy to follow, and designed to minimize side effects.
This is a “heavy-duty” diet. We developed specifically for patients with chronic & severe SIBO infections. Meaning – patients who’ve been struggling for YEARS & had every other treatment method & drug they tried fail them (or had the problem came back).
It is a gentle yet effective diet.
We’re confident that once you’ve completed it, SIBO will be much easier to manage.
We’re not going to go too in depth into listing every specific food you can and can’t eat for SIBO.
You’ll get a food list, grocery guide, recipe book & everything else you’ll need on the bottom of this page as part.
Don’t Forget to Grab Our 2 Free SIBO eBooks
These are 2 super-detailed mini ebooks that cover everything you need to know to put SIBO behind you – including a step-by-step diet plan, 25 different food lists, what foods to eat & avoid, a grocery shopping guide & a whole lot more.
Click Here Now To Grab Both of These PDF’s For Free
This includes:
- The CanXida Protocol: 3-Phase SIBO Diet & Food List — Based on 30 Years of Experience (64 pages)
- 21-Days To Fix Your Gut Health: A Step-By-Step Guide to Healing Your Gut of Candida, Leaky Gut, IBS & Almost Any Other (67 pages)
Click Here Now To Grab Both of These PDF’s For Free
And yes, they’re really free. You don’t even have to buy anything to access them. They’re just one of the many free resources we created to help people like you.
Should You Follow the FODMAP Diet For SIBO? Pros & Cons
If you’ve been sick with SIBO for a while, chances are you’ve heard of the FODMAP diet before. A lot of SIBO websites today promote the FODMAP approach.
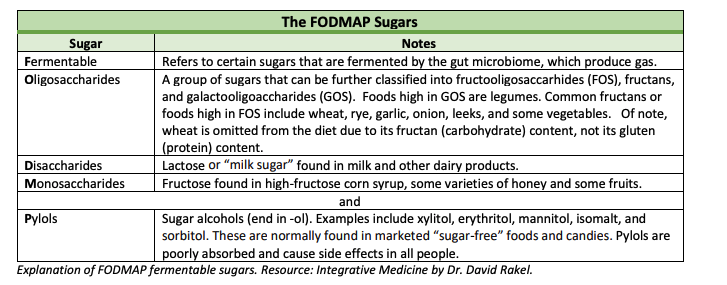
FODMAP refers to:
- Fermentable
- Oligosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Monosaccharides
- Pylols
Which are different types of fermentable sugars. The chart below explains it in more detail:
We’re not really fans of the FODMAP approach at CanXida. We’ve seen far too many people make mistakes with this diet.
It’s a very restrictive diet and can produce negative results if you stay on it for too long.
Many patients think they need to be on the FODMAP diet long term. They take too many carbohydrates out of their diet.
You shouldn’t be on a FODMAP diet for months on end. Remember, we shape our microbiome & gut bacteria by what we eat. So the more restrictive you are with food, the more restrictive the bacteria will become in the gut.
And over time this is going to create dysfunction. It’s going to create a situation where if you deviate off it, you’ll get sick rather quickly. Which of course will make you think “I need to get back on the FODMAP diet.”
We’ve had one patient in particular who stayed on FODMAP for over 2 years, and she looked quite sick as a result.
If you’ve already started a FODMAP diet that’s fine. Just remember that it’s a short phase you go through to find out what foods you need to eliminate prior to starting your treatment.
Instead of FODMAP, we like to put SIBO patients on a 3 phase diet that looks like this:
- Step 1: The MEVY Diet (3 – 4 weeks)
- Step 2: The Low Allergy Diet (2 – 8 weeks)
- Step 3: The Food Re-introduction Stage (2 – 4 weeks)
The first phase is called the MEVY (Meat, Eggs, Vegetables & Yogurt) diet. Which is far less restrictive and safer to stick to long term (if you so desire) than FODMAP.
You can follow to the MEVY diet for months if you like. It’s not going to cause problems like FODMAPs would.
If this is your first attempt at a SIBO diet, we recommend you go through something we call “The 14 Day Big Cleanup” before you start Phase 1: The MEVY Diet.
The 14 Day Big Clean-Up
The 14 Day Big Clean-UP is sort of like a Phase 0.
It serves 2 purposes. First it allows you to slowly ease yourself into the new diet without experiencing withdrawal from things like alcohol, caffeine, take-out foods, candy, ice cream & chocolate.
It also reduces your chances of experiencing die-off symptoms during the diet.
This might sound odd but you’ll likely need to get rid of a lot of the foods in your kitchen pantry during this step. The more severe your SIBO & the worse your symptoms are, the more CRITICAL this step is.
The best thing to do is grab a big bag and fill it with all the foods that have been sitting in jars or bottles in your fridge. If you haven’t looked at or touched them for a long time, they NEED to go. Get rid of sauces, syrups, jams, etc. All these tend to be stored for long periods & develop mold.
Even if you can’t visibly see any mold, don’t take any chances. Throw it away.
Next you want to get rid of anything containing white sugar, high fructose corn syrup, and especially artificial sweeteners because these will prevent your recovery like nothing else. You need to give the candy away, the ice cream, the cookies. All that stuff needs to leave your home. That way you won’t be tempted by it later.
Same goes for highly processed foods like potato chips, microwave meals, deli meats, pastries, etc. Give it away to a neighbor or friend or just throw it in the trash.
As you likely know, these are the foods bacteria in the small intestine thrive on. By removing these foods from your diet, you take away its food source. This leaves the bacteria weakened & far easier to get rid of later.
If you don’t want to do this & wish to continue eating these foods (even in small amounts) during the diet, you may as well stop reading this now. It’s that important.
Do this over a period of a few days if you must, but get it done.
Here’s a short list of foods to get rid of:
- Soda drinks
- Chocolate (even unsweetened or 100% cacao)
- Ice cream
- Sweets or candy
- Biscuits or cookies
- Donuts, muffins or cakes
- Pastries
- White breads
- Chips
- Pizza, fried chicken & any take-out foods
- Nutella, peanut butter, jam or spreads (unless you make them yourself)
For more information about the Big Cleanup, watch the video below:
Step 1: The MEVY Diet (Meat, Eggs, Vegetables & Yogurt)
MEVY stands for Meat, Eggs, Vegetables & Yogurt.
This is a well tested diet designed to bring your intestinal flora back into balance. It calms and heals your gut from a multitude of conditions including candida overgrowth, SIBO, parasite infections and more.
We didn’t create this diet.

It’s been around for a long time. Since at least 1986 when it was recommended in “The Yeast Syndrome” by Dr. Morton Walker. You don’t need to read it. You’ll learn everything you need about the MEVY Diet through this page & our YouTube channel.
The MEVY diet is a short term diet. You only need to be strict with it for 3 to 4 weeks. For best results, follow it strictly for at least 2 weeks. Then you can loosen up a little for the next 2 to 3 weeks as you start to implement the Low-Allergy diet (this is step 2).
It’s up to you to decide how long you want to stay on the MEVY approach.
Either way, we can assure you of one thing—the MEVY Diet is highly effective. It’s designed to help quickly alleviate most, if not all, digestive disturbances you may be experiencing.
It’s a tasty and healthy diet. You’re not going to starve or feel deprived.
Meats generally are not favored at all by bad bacteria and yeast.
You’re not going to have a problem with fresh fish, lean beef, or free range eggs. Just be careful not to overload your diet on red meat because that can cause constipation and clogged up bowels.
If you’re a vegan there’s plenty of other options you’ve got.
These foods also discourage bad bacteria like Citrobacter freundii and Blastocystis, pseudomonas, and all kinds of other nasty bacteria and micro-parasites typically found in people who’ve had SIBO for a long time.
The MEVY diet is a low-carb diet.
The MEVY Diet has existed well before low-carb diets became popular. Unlike other low-carb approaches, its primary goal isn’t weight loss—though you may naturally shed excess weight if followed closely.
Don’t worry about keeping track of the specific foods you can and can’t eat on the MEVY Diet. You’ll get all that stuff in the PDF guides at the bottom of this page.
You’re allowed to eat all meats, eggs, most vegetables (except high starch vegetables like potatoes, carrots, pumpkin, sweet potato, peas, corn and beets) and plain yogurt.
Eliminate foods such as heavily processed cereals, pasta, conventional breads (which contain yeasts and sugars), pastries, chips and alcohol. Alcohol is a big one. If you can’t make a commitment to stop drinking alcohol (even one glass of wine a week) for a period of at least 6 months, you need to stop reading this page.
Alcohol has a very powerful effect on gut bacteria & will prevent your recovery the same as eating donuts on a regular basis will. If your goal is to restore your levels of beneficial bacteria, the alcohol NEEDS to go. Most patients who are serious about getting their health back are willing to take a break from alcohol for a while.
You can go back to drinking wine on the weekends once your health is back to normal again.
Sourdough bread is OK to eat, especially rye. You also want to avoid all dairy products, with natural unsweetened yogurt being the only exception.
Some experts believe it’s best to go on a completely grain free “Specific Carbohydrate Diet” (SCD). But we don’t believe SCD diets are the way to go for SIBO.
SIBO varies from person to person. We’ve had some patients who could handle fruits just fine. While others would feel sick and get gas after eating any fruit at all.
A big tip is to try modifying starches. As in, try cooking different starches in different ways. We’ve had several patients say they would tolerate steamed grains really well for example. But if they didn’t steam them, they’d get a bad reaction.
We’ve seen similar things with potatoes and starchy vegetables. Some patients can tolerate them just fine when they bake them, but couldn’t tolerate them when cooked via a different method.
We’ve also had patients who could tolerate brown or black rice. But as soon as they added any jasmine or basmati rice, they’d get immediate bloating and gas.
So don’t automatically assume because you’ve got SIBO that you have to avoid every kind of starchy vegetable or grain. Experiment and see what works for you.
Step 2: The Low Allergy Diet (Restores Your Gut’s Immune System)
Once you’ve been on the MEVY Diet for a few weeks, we start the Low Allergy Diet.
The purpose of this diet is to restore your gut’s immune system.
This step is crucial for anyone with SIBO & a history of antibiotic use. Especially if you’ve got low levels of good bacteria and all sorts of gastrointestinal distress.
That’s why it’s best to come off what are considered key allergy foods.
These Foods Are:
- citrus (especially oranges)
- pineapple
- banana
- shellfish
- peanut/peanut butter
- wheat/gluten
- chocolate
- cow’s milk
Cow’s milk is a big one.
We’ve seen testing on over 350 young children that found nearly 70% had a problem with cow’s milk. Bananas came back around 14%. Pineapples and shellfish came back nearly 20%.

Bread and gluten allergies are not as common as you think.
Chocolate however is. Even dark chocolate, 70% cocoa or whatever it is, it’s GOT TO GO for a while. There’s no way around it. Chocolate aggravates IBS & other gut disturbances. Even if it’s raw cacao you need to take it out of your diet for at least 3 to 4 weeks.
We’re not big fans of telling people to eliminate wheat or gluten from their diet forever.
In fact, we’ve seen people get BACK into gluten after they were told by doctors they could NEVER eat wheat ever again. Because once your gut bacteria levels are restored – gluten is no longer a problem.

Just because every blog site out there says you should eat gluten-free doesn’t make it true. “Gluten free” is almost like a religion today.
Remember, only 1 or 2% of the population has Celiac Disease.
Are you celiac? Probably not. Are you gluten intolerant? Probably not.
Do you have a disturbed gut microbiota? Probably yes.
What we’re doing with the Low Allergy Diet is taking out the foods that could potentially trigger an immune response.
This is very smart because you’ve likely got food allergies and intolerances right now that are creating immune dysfunction.
By taking all these foods out, it stops the immune system from reacting.
That way, once your digestion is in better shape, you’ll be able to eat these foods without having to worry whether the next bite of the “wrong food” will send you running to the toilet or cause gas, bloating or other symptoms.
All you do at this stage is remove the foods listed previously in this section, and keep it that way for a period of several weeks to several months. You should continue to eat the MEVY Diet in the meantime (although you don’t have to be as strict with as you were in the beginning).
Step 3: The Food Reintroduction Phase
At this point you should be feeling a lot better and much of your gut disorder symptoms should have disappeared. So we can start reintroducing the foods we eliminated in phase 1.
You’ll get the exact details once you download the free PDF report at the bottom of this page but what you’ll basically do is get a piece of paper and write down all the foods you really love but feel you can’t eat because they give you problems.
We’re talking about ice cream, beer, wine, pizza, chocolate chip cookies, pastries, whatever you like.
Then what you’ll do is slowly start to reintroduce these foods & see what effect they have on you.
Yes, even ice cream and pastries. We don’t like being the “food police.” If you like, you can choose healthier versions of them like oat milk ice cream vs a cheap dairy one.
It may be surprising, but after completing our diet plan, you’ll likely find that many of the foods on your ‘to avoid‘ list no longer cause issues.
Of course this doesn’t mean you can go on a 100% junk food diet and expect to stay healthy, but you can be sure an occasional ice cream or pizza with friends isn’t going to bother you anymore.
You don’t have to be gluten, dairy, sugar, alcohol or whatever else free for the rest of your life.
We can tell you now after helping THOUSANDS of folks overcome chronic gut problems – PEOPLE GET SICK AND TIRED of having these restrictive diets.
They hate it.
Every label has got to be scrutinized rigorously. Every time you go out with friends 90% or more of the menu is off limits and you’re stuck with the blandest salad. What a pain in the butt!

A Precaution About Reintroducing Foods:
The first foods you reintroduce are NOT the foods you love the most.
You want to start with the foods you feel a bit indifferent about.
You haven’t eaten them in a while but you could take them or leave them.
It could be carrots or it could be some fish. If you really love some particular food, it’s not a good idea to introduce it back into the diet right away on day 1. You can bring them in after a few days or a few weeks.
If you bring those foods back in the diet too quickly, there’s a possibility you’re going to overeat and have too much of them. And then you can get your blood sugar worked up and this can push you off-track.
We’ve seen this happen again and again, so just take it slow and you’ll be fine.
To conclude, as you begin reintroducing foods slowly and thoughtfully, building a strong foundation of gut health knowledge can make all the difference. To support your journey, we’ve handpicked some essential readings below.
Essential Reads for Your SIBO Journey
- Are Supplements Necessary For Gut Issues Such as Candida, SIBO, & IBS Or Can You Fix These Issues With Diet Alone?
- Are Herbal or Natural Remedies or Supplements Actually Effective Against Chronic Gut Issues Such as Candida Yeast Infections, SIBO, IBS or Parasites?
- Natural Antifungals, Antibacterials & Anti-parasite Supplements vs Probiotics (& Why You Want to Take BOTH at the Same Time)
- How to Choose a Gut Cleaning Antifungal, Antibacterial or Anti-parasite Supplement that Actually Works & Skip the Junk
- Why Most People Get Nowhere With Probiotics & 5 Things to Look For When Choosing a Probiotic For Candida, SIBO, IBS & Other Gut Issues
Don’t Forget to Grab Our 2 Free SIBO eBooks
These are 2 super-detailed mini ebooks that cover everything you need to know to put SIBO behind you – including a step-by-step diet plan, 25 different food lists, what foods to eat & avoid, a grocery shopping guide & a whole lot more.
Click Here Now To Grab Both of These PDF’s For Free
This includes:
- The CanXida Protocol: 3-Phase SIBO Diet & Food List — Based on 30 Years of Experience (64 pages)
- 21-Days To Fix Your Gut Health: A Step-By-Step Guide to Healing Your Gut of Candida, Leaky Gut, IBS & Almost Any Other (67 pages)
Click Here Now To Grab Both of These PDF’s For Free
And yes, they’re really free. You don’t even have to buy anything to access them. They’re just one of the many free resources we created to help people like you.
